4 differences between gas booster pump and gas-liquid booster cylinder
Gas booster pumps and gas-liquid booster cylinders are two common machines in the oil and gas industry. Many people can’t tell the difference between the two. The following will introduce their four major differences.
Differences in working principle
- Working principle of gas booster pump
This kind of piston booster pump with compressed air is the power source, when the intake air is, the spool of the booster air control valve switches back and forth to control the piston of the booster valve at an extremely fast speed. Making a reciprocating action, as the output pressure increases, the reciprocating speed of the piston slows down until it stops. At this time, the output pressure of the booster valve is constant, the energy consumption is at a minimum, and each component stops working; no matter what causes the pressure of the pressure-holding circuit to drop, the booster valve will automatically start to supplement the leakage pressure and keep the circuit pressure constant.
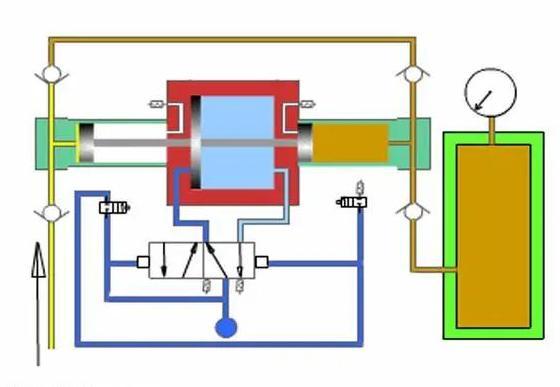
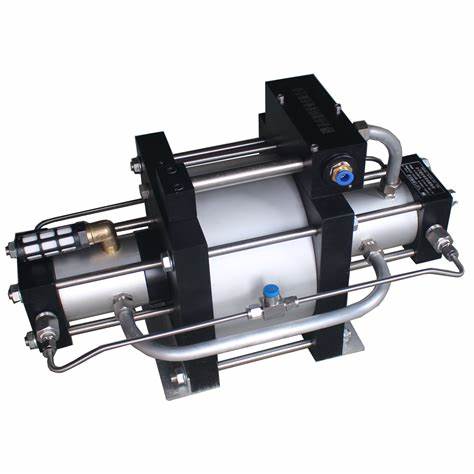
- The working principle of the gas-liquid booster cylinder
The gas-liquid booster cylinder is an integrated combination of a hydraulic cylinder and a supercharger, using the ratio of the different pressure cross-sectional areas of the supercharger and the pascal energy balance principle works. Because the pressure does not change, when the pressure area changes from large to small, the pressure will also change with the size, so as to achieve the pressure effect of increasing the air pressure dozens of times. Take the pre-pressure booster cylinder as an example: When the working air pressure is pressed on the surface of the hydraulic oil (or piston), the hydraulic oil will compress the air and flow to the pre-pressing stroke chamber. At this time, the hydraulic oil will rapidly push the type of parts to make displacement. When the working displacement encounters resistance greater than the air pressure, the cylinder Then stops the action. At this time, the booster cavity of the booster cylinder starts to pressurize due to the action of the electrical signal (or the pneumatic signal) to achieve the purpose of forming the product.
Different product categories
The gas booster pump is mainly divided into single-head single-acting pumps, double-head single-acting pumps, and double-head double-acting pumps. The multiples are 5, 10, 15, 25, 40, 60, and 100 times, with nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and special gases.
The gas-liquid booster cylinder is mainly divided into direct pressure type and pre-pressure type, which can be divided into standard type, horizontal installation type, adjustable pre-pressure type, adjustable pressure-boosting type, and adjustable pre-pressure and boosting type, fast type, mini type, side by side, flip type and so on.
Differences in selection details
The selection of a gas booster pump needs to provide the use medium, booster ratio, flow requirements after high pressure, etc. For example, if the boosting medium is air/nitrogen, we choose it in the air booster pump/nitrogen booster pump; if the boosting medium is liquid, we will choose it in the pneumatic liquid booster pump. In addition, it should be noted that we usually choose a pump with a boost ratio slightly higher than the calculated value to ensure that our pump can output the pressure required by the system under normal conditions.
The commonly used parameters for the selection of gas-liquid booster cylinders include product installation method requirements, product output tonnage requirements, product total stroke requirements, product preload stroke requirements, product booster stroke requirements, and product stroke requirements. There is an adjustment method (mechanical adjustable or magnetic adjustable, etc.), product lifting force (return pull force) size requirements, etc. In addition to the parameters of the gas-liquid booster cylinder product itself, there are other parameters such as the pressure of the gas source used on site, the space requirements for on-site installation, and the frequency of product use. Only by combining all the parameters, can the model be selected more accurately to avoid the product not being used normally due to wrong model selection.

Differences in applications
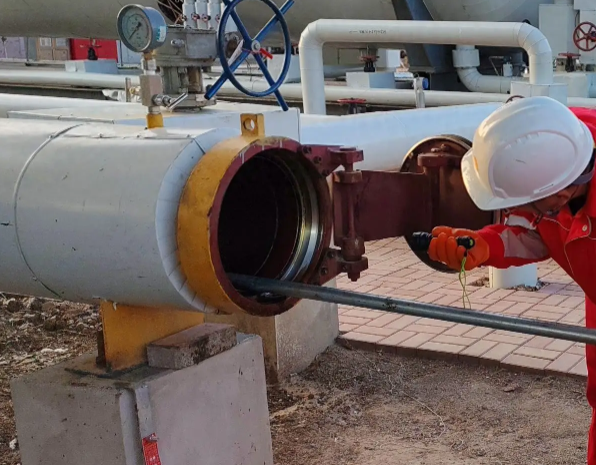
The gas booster pump increases the pressure of the gas source and is driven by compressed air. It is generally used for blasting and pressure testing of pressure vessels, instruments, pipe fittings, valves, etc. Gas stability; safety valve calibration; high-pressure gas system and instrument testing; meet all equipment requirements for high pressure, etc.
The gas-liquid booster cylinder adopts a gas-liquid combination, no hydraulic unit is needed, advanced “soft in place” and unique “strength self-adaptive” stamping technology, fast action, and large output (1~200t), adjustable pressure stroke, Soft landing does not damage the mold, energy saving, and environmental protection, generally used in bending, printing, bending, pressing, punching, punching, extrusion molding, forging, riveting, forming, cutting and other occasions.






